
Russia’s aggression against Ukraine and Georgia, its vast military modernization program, its violation of the INF treaty, and Vladimir Putin’s clear nostalgia for the former Soviet Union have made it clear that a new Cold War has emerged.
![]() In response, NATO has been adjusting to the new threat level. NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg stated this month that “We have seen a much more assertive Russia, we have seen a Russia which has over many years invested heavily in their military capabilities, modernized their military capabilities, which are exercising not only conventional forces but also nuclear forces, and which has been willing to use military force against a neighbor: Ukraine. And of course, NATO has to be able to respond to that and we have responded to that partly with our enhanced Forward Presence with more deployment of troops in the eastern part of the alliance, but also by increasing the readiness of our forces and also increasing our ability to move forces. And we are constantly adapting and what we do in Europe now is part of that adaptation.”
In response, NATO has been adjusting to the new threat level. NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg stated this month that “We have seen a much more assertive Russia, we have seen a Russia which has over many years invested heavily in their military capabilities, modernized their military capabilities, which are exercising not only conventional forces but also nuclear forces, and which has been willing to use military force against a neighbor: Ukraine. And of course, NATO has to be able to respond to that and we have responded to that partly with our enhanced Forward Presence with more deployment of troops in the eastern part of the alliance, but also by increasing the readiness of our forces and also increasing our ability to move forces. And we are constantly adapting and what we do in Europe now is part of that adaptation.”
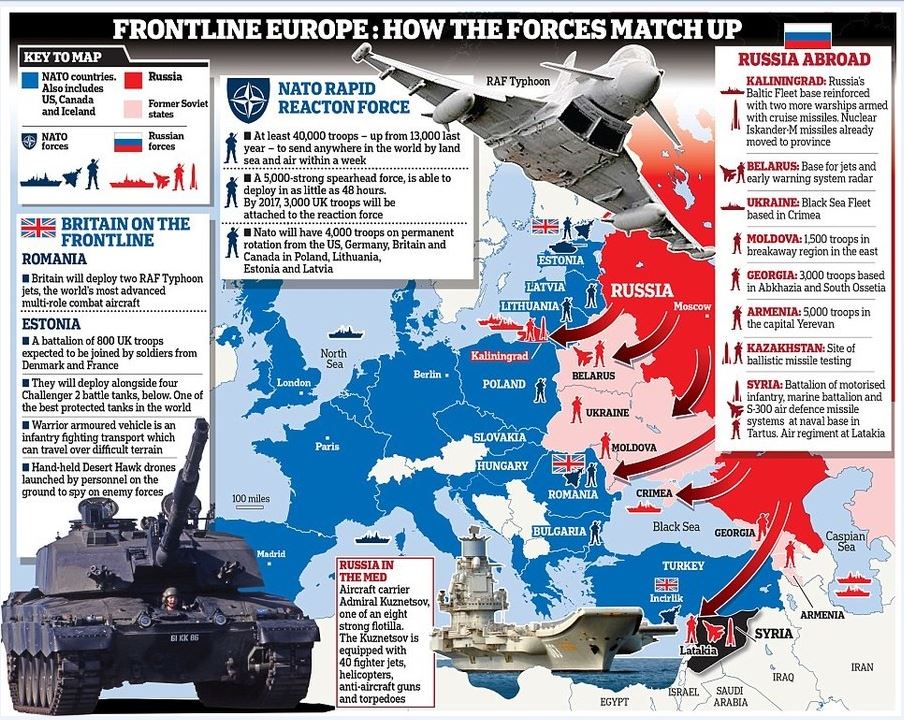
Frontline Europe. Credit: funnyjunk.com
At the end of the recent NATO defense ministers meeting earlier this month, Stoltenberg noted that “At the Warsaw Summit last year, we decided to launch an assessment of the NATO command structure in light of the changed security environment. To ensure it can do the job across the full spectrum of Alliance missions…we agreed on the outline design for an adapted NATO Command Structure, which will be the basis for further work.”
Two new commands will be created:
A Command for the Atlantic, to ensure that sea lines of communication between Europe and North America remain free and secure, and a new Command to improve the movement of military forces across Europe. And ways to strengthen the logistical function across the NATO Command Structure.
“Other moves approved by the Defense Ministers included increased attention to cyber warfare, including the creation of a new Cyber Operations Centre to help integrate cyber into NATO planning and operations at all levels, and an increase in the size of the alliance’s Resolute Support training mission in Afghanistan from, approximately 13,000 to about 16,000 individuals.”
Stoltenberg also emphasized that “We must be just as effective in the cyber domain as we are on land, at sea and in the air, with real-time understanding of the threats we face and the ability to respond however and whenever we choose.”
NATO is changing in a number of ways, some encouraging for the alliance, and some that are frankly worrisome.
Under the leadership of Turkey’s President Recep Erdogan, a nation that was once considered a key anchor in NATO’s south, and, before the end of the cold war, the only NATO ally directly bordering the USSR, continues to drift away. The latest indication is his purchase of a Russian Air Defense System, Moscow’s S-400. The move has been soundly criticized by the United States.
But as Turkey becomes increasingly estranged, other nations are moving closer. Sweden, notes RT, recently played host to around 2,000 NATO personnel,” more than 1,400 of whom are from the US, according to the local Sydöstran newspaper. NATO members Denmark, Estonia, France, Lithuania, and Norway are also participating, as well as non-aligned Finland.”
Within the Middle East, Israel may be moving closer to NATO. According The Times of Israel, Gadi Eisenkot, head of the Israeli Defense Forces, made an undeclared trip to NATO headquarters in Brussels to speak with the top US general in Europe. Regional developments were reportedly discussed. A key part of the discussion “included Iran’s alleged construction of a military base less than 50 kilometers (30 miles) from Israel’s Golan border.”
Frank Vernuccio serves as editor-in-chief of the New York Analysis of Policy and Government.
















Follow Us